
What is.....
Cannabis is an herb, original from Central Asia, that has been used by humans for approximately 10,000 years for industrial, medicinal and recreational purposes.
Although the classification of cannabis in the tree of life has been revised multiple times, currently all the varieties of cannabis are considered one species, Cannabis sativa L.
Historically, multiple subspecies and varieties have been described in Asia and Europe, including Cannabis sativa subspecies sativa, C. s. subsp. indica, C. s. subsp. ruderalis, C. s. subsp. indica variety afghanica, etc., which could be distinguished from each other based on their growing habits, leaf and flower shapes and colors, and the concentration of intoxicating and non-intoxicant chemicals present in their flowers and young leaves.

What are the uses of hemp?
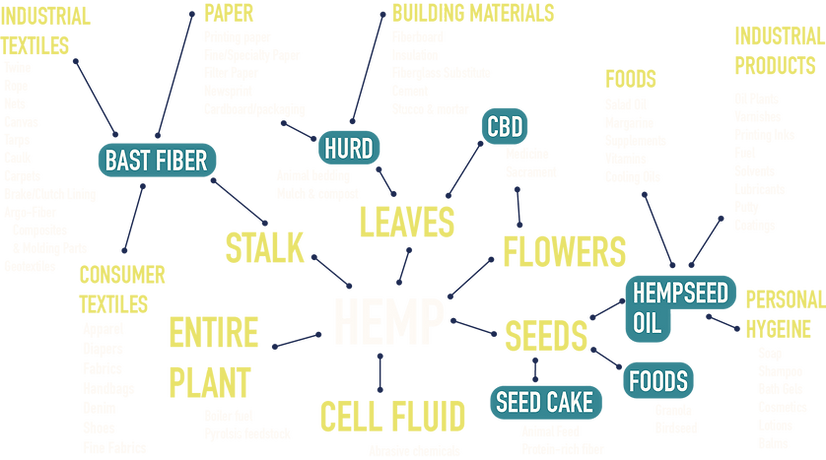
Hemp can be produced to obtain fiber, grain, and phytochemicals. Hemp fiber is used for many industrial purposes, including production of textiles, paper, construction materials (hempcrete, hemp wood flooring, thermal insulation materials, etc.), animal bedding, bioplastics, among others. Hemp grain can be used shelled for food (hemp hearts) or hulled as animal feed (at this time only poultry in Pennsylvania) or for extraction of seed oil. Hemp seed oil is edible and rich in nutrients, but it burns easily, so it is often used in salad dressings or as an ingredient in health products, food, supplements and cosmetics, as well as for other industrial applications.
Hemp flowers and the young leaves around them are rich in chemicals (cannabinoids and terpenes), particularly before they are pollinated. Cannabis produce chemicals in small glandular hairs known as trichomes. Trichomes produce hundreds of chemicals, among which the most valuable are cannabinoids and terpenoids, also known as terpenes. Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are the most abundant cannabinoids in hemp, while β-Caryophyllene and β-myrcene are the most abundant terpenoids in hemp. Both cannabinoids and terpenoids have been studied for their potential beneficial properties.
WHY IS INDUSTRIAL HEMP CONSIDERED A SUSTAINABLE FIBER?
Hemp is considered a highly sustainable source of fiber and other biomass raw materials due to the fact that it grows quickly in most climates with little need for irrigation, pesticides or fertilizers. It takes up relatively little space and produces more biomass per acre than trees and most other fiber-producing plants. Hemp crops even give back by returning nutrients to the soil and sequestering carbon more efficiently than most other agricultural crops. Finally, virtually every part of the plant can be used, which minimized the amount of agricultural waste produced.
IS HEMP A STRONG FIBER? WHAT IS THE TENSILE STRENGTH?
While natural fiber strength varies greatly depending on plant varietal and growing conditions, hemp is considered one of the strongest natural fibers. Hemp fiber is reported to have a tensile strength ranging from 500 to 1,100 MPa, which compares favorably with published values for fibers such as jute (400-800 MPa), sisal (500-850 MPa), flax (350-1,800 MPa) and ramie (400-900 MPa).
HOW MANY HEMP FARMERS DO WE HAVE NATIONALLY?
In 2020, a total of 21,496 growers were permitted to grow hemp in the United States, a 27% increase compared to 2019. This translated to a total acreage of about 450,000 acres in the 2020 production season.
HOW MANY HEMP FARMERS DO WE HAVE IN PA?
The PA hemp program started in 2017 with 14 growing permits issued by the PA Department of Agriculture for research purposes, In 2020 they issued 510 growing permits and an additional 65 processing permits.
WHAT IS THE HEMP GROWTH CYCLE AND TIMEFRAME?
The hemp plan growing cycle can be as short as 120 days, depending on climate and growing conditions. This makes it possible to grow 2 crops in one growing season, or to serve as a seasonal rotational crop.
WHAT ARE THE IDEAL CONDITIONS TO GROW HEMP?
Due to the large number of varietals of hemp that are available (more than 400 have been cataloged), some variety of hemp can be grown in almost any agricultural climate.
Information on the Cannabis plant is kindly provided in part by Dr. Carla Garzon and her research assistant Danielle Bowman, Plant Science and LAES Department, Delaware Valley University
For more information, reach out to us on our Contact page.


